Breastmilk is the best for babies. The World Health Organisation recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life. Unnecessary introduction of bottle feeding or other food and drinks will have a negative impact on breastfeeding. After six months of age, infants should receive age-appropriate foods while breastfeeding continues for up to two years of age or beyond. Consult your doctor before deciding to use infant formula or if you have difficulty breastfeeding.
- Week 1
- Week 2
- Week 3
- Week 4
- Week 5
- Week 6
- Week 7
- Week 8
- Week 9
- Week 10
- Week 11
- Week 12
- Week 13
- Week 14
- Week 15
- Week 16
- Week 17
- Week 18
- Week 19
- Week 20
- Week 21
- Week 22
- Week 23
- Week 24
- Week 25
- Week 26
- Week 27
- Week 28
- Week 29
- Week 30
- Week 31
- Week 32
- Week 33
- Week 34
- Week 35
- Week 36
- Week 37
- Week 38
- Week 39
- Week 40
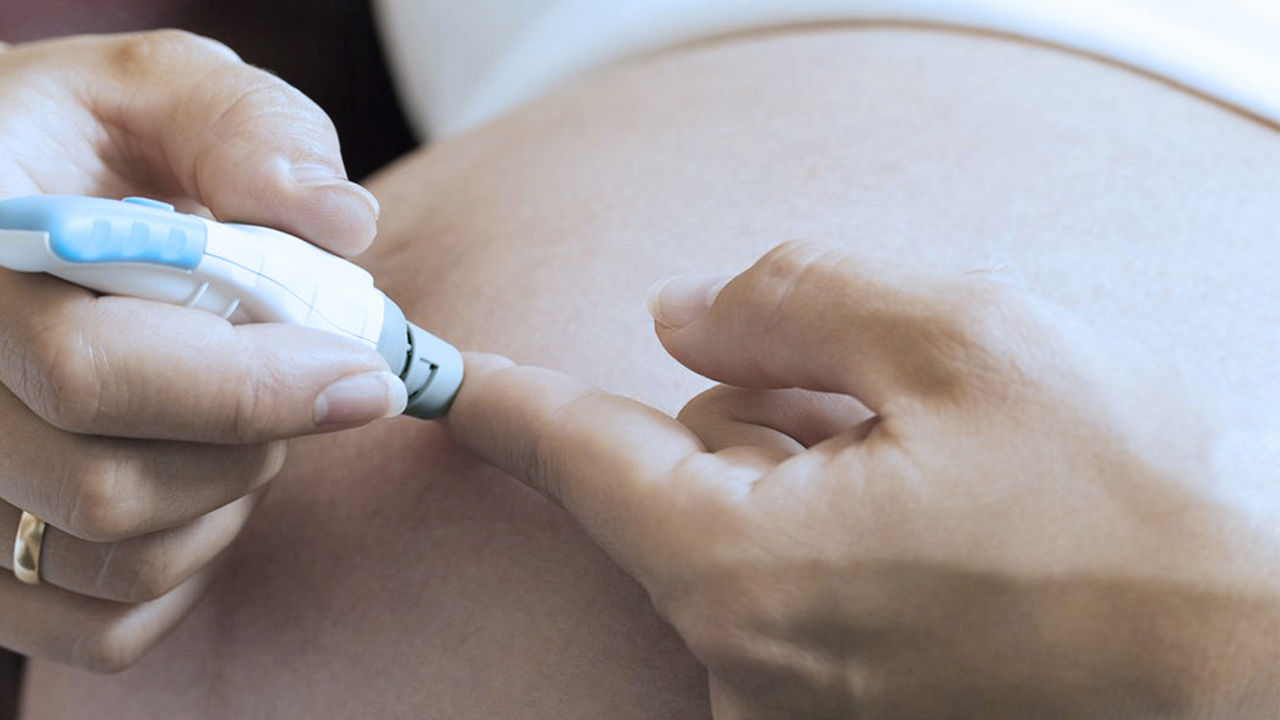
Gestational diabetes occurs in approximately 2-5% of pregnancies in Singapore. However, there could be more pregnant mothers’ left undiscovered, suffering from this condition* Read here to learn how to reduce the risk of gestational diabetes.
What causes gestational diabetes?
The hormone insulin is responsible for the metabolism of excess sugar which is not needed by the body. Your pregnancy hormones such as estrogen, placental lactogen and progestins may be the culprit that affects your metabolism, including sugar metabolism. The disruption of the sensitivity of insulin production can occur from the 2nd half of the pregnancy. The result of the rise in blood sugar during pregnancy is known as gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes occurs mainly in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Women who are overweight, who have suffered from earlier gestational diabetes or have history of diabetes mellitus, or family history of diabetes, are especially prone to gestational diabetes. It is advisable to go for a blood glucose test to detect any possibility of diabetes at an early stage. Some women will recover from gestational diabetes as soon as their hormonal levels return back to its original levels.
How does gestational diabetes affect my pregnancy?
Nevertheless, gestational diabetes should not be taken lightly. It can cause high blood pressure for the long term if remains undetected. It increases the risk of urinary tract or vaginal infections, which in turn can trigger premature labour. In addition, children of diabetic mothers are significantly heavier at birth. This happens due to the increased sugar levels of their babies caused by the elevated blood sugar levels of the mother. This will in turn cause their babies to have an increased likelihood of being overweight in their adulthood and develop Type 2 diabetes. However, not to worry as if gestational diabetes is treated well, you can help to reduce the risks of your child suffering from these conditions.
How can you prevent gestational diabetes?
The most effective measure against gestational diabetes is to have optimal nutrition during your pregnancy, regardless of whether you belong to a group at risk of diabetes or not. Have a healthy and well-balanced diet. Consult your doctor or speak to your midwife if you are unsure.
If you are heavier than your ideal weight, you should try to lose some weight before conception as dieting is not advisable during pregnancy. Even a few pounds less can help to reduce the risk of developing gestational diabetes. If you are already pregnant and are overweight, it would be ideal to gain no more than 7 kilograms up to birth.
What do I do if gestational diabetes is detected?
If you find yourself having an elevated blood glucose level, you should pay attention to your diet, keep it healthy and well-balanced in order to keep your condition under control. This is very important – even when most babies of mothers with gestational diabetes are healthy when they come into the world. Your doctor will advise you.
Approximately 85 percent of all pregnant diabetic women are able to control their blood sugar well with proper diet. Only about 15 percent of women require insulin treatment. The doctor also recommends adequate exercise.
Ideal sports for pregnant women
A 30-minute easy endurance training is an ideal sport for pregnant women, to assist in lowering blood sugar levels.
Actively counteracting gestational diabetes
A healthy diet that can regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
You can actively counteract gestational diabetes with proper nutrition. You should consistently avoid sugary foods and including carbohydrates in your diet is fine. Moreover, you should consume high-fibre foods such as whole wheat bread, cereals, brown rice, whole wheat pasta, legumes, fruits and vegetables. Some of these foods are digested slower and thus delay the sugars from these carbohydrates to be released into the blood stream. In contrast, low-fibre grain products such as white breads or rolls allow the sugars to be quickly released into the blood stream, and therefore should be excluded from your diet. You should also attempt to distribute your intake of carbohydrate-containing foods, 5 to 6 small meals per day. This allows you to control the rise in blood sugar levels after meals. Find out more on having ideal “Nutrition” during your pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes can disappear just as quickly as after birth. In many cases, it leaves positive traces of occurrence of future diabetes. Therefore, it is always important to be aware of your diet and eat healthily.
* Sources from HPB
Join our AptaAdvantage Club today to enjoy:
- Educational content to support you on your motherhood journey
- Various complimentary classes and exclusive discounts with our key enrichment partners
Kickstart your AptaAdvantage experience by signing up HERE.
Related articles

Connect with our team of experts
We provide advice and support for you on your parenthood journey